The derivative (or differentiation) of cot x is equal to -cosec2 x. Let’s learn how to find the derivative of cot x using the following method of derivatives:
- First principle of derivatives
- Product rule of derivatives
- Quotient rule of derivatives
- Chain rule of derivatives.
Table of Contents
What is the Derivative of cot x?
The derivative of cot x is denoted by the symbol $\frac{d}{dx}$(cot x) or (cot x)$’$ and it is equal to -cosec2 x. Note that cotx can be expressed as the quotient cosx/sinx. This can be used to find the derivative of cotx using the product rule and the quotient rule of derivatives together with the trigonometric formulas.
Derivative of cot x Formula
Derivative of cot x Formula: The derivative formula of cot x is given below
- d/dx(cot x) = -cosec2 x
- (cot x)$’$ = -cosec2 x
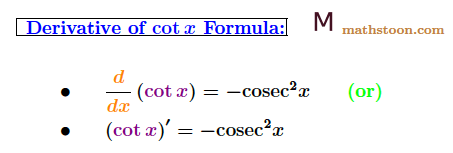
Derivative of cot x by First Principle
We will now prove the derivative of cot x is -cosec2 x by limit definition. Let’s put $f(x)=\cot x$ in the first principle of derivatives formula which is given below.
$\dfrac{d}{dx}(f(x))$ $=\lim\limits_{h\to 0}\dfrac{f(x+h)-f(x)}{h}$
Thus we have:
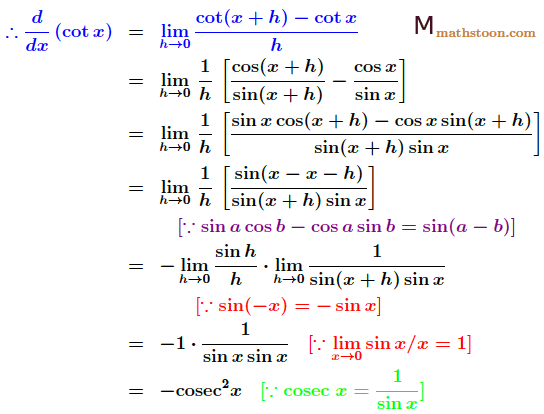
So the derivative of cotx by first principle is equal to -cosec2x.
Also Read:
| Derivative of tanx | The derivative of tanx is sec2x. |
| Derivative of log3x | The derivative of log3x is 1/x. |
| Derivative of sin2x | The derivative of sin2x is 2sinx cosx. |
| Derivative of 1/x | The derivative of 1/x is -1/x2. |
Derivative of cot x by Product Rule
To obtain the derivative of cotx by the product rule, let us first recall it. For two functions f(x), g(x), the derivative formula of the product fg is known as the product rule of derivatives which is given below:
$\dfrac{d}{dx}\left(fg \right)=f \dfrac{dg}{dx} + g \dfrac{df}{dx}$
To prove the derivative of cot x is -cosec2 x by the product rule, we will follow the below steps:
Step 1: At first, we express cot x as the product of two functions as follows
cot x =$\dfrac{\cos x}{\sin x}$ = cos x ⋅ cosec x
∴ $\dfrac{d}{dx}(\cot x)$ $=\dfrac{d}{dx}$(cos x ⋅ cosec x)
Step 2: Now we use the above product rule of derivatives. So we have
$\dfrac{d}{dx}(\cot x)$ = cos x $\dfrac{d}{dx}$ (cosec x) + cosec x $\dfrac{d}{dx}$(cos x)
= cos x ⋅ (-cosecx cotx) + cosec x ⋅ (-sin x)
$=-\cos x \cdot \dfrac{1}{\sin x} \cdot \dfrac{\cos x}{\sin x}$ $-\dfrac{1}{\sin x} \cdot \sin x$
$=-\dfrac{\cos^2 x}{\sin^2 x}+1$
$=-\dfrac{\cos^2 x+ \sin^2 x}{\sin^2 x}$
$=-\dfrac{1}{\sin^2 x}$ [∵ sin2 x+cos2 x=1]
= -cosec2x.
So the derivative of cot x by the product rule is -cosec2 x.
Derivative of cot x by Quotient Rule
The quotient rule of derivatives says the following: $\dfrac{d}{dx}\left(\dfrac{f}{g} \right)=$ $\dfrac{g\frac{df}{dx}-f\frac{dg}{dx}}{g^2}$, where f and g are two functions of x.
To prove the derivative of cot x is -cosec2 x by the quotient rule of derivatives, we need to follow the below steps.
Step 1: Express cot x as the quotient of two functions. Note that we have
cot x = $\dfrac{\cos x}{\sin x}$
∴ $ \dfrac{d}{dx}(\cot x) = \dfrac{d}{dx}(\dfrac{\cos x}{\sin x})$
Step 2: Use the above quotient rule of derivatives.
$\dfrac{d}{dx}(\cot x)$ $={\small \dfrac{\sin x \frac{d}{dx}(\cos x)-\cos x\frac{d}{dx}(\sin x)}{\sin^2 x}}$
Step 3: Simplify the above expression.
$=\dfrac{-\sin x \sin x-\cos x \cos x}{\sin^2 x}$
$=-\dfrac{\sin^2 x+\cos^2 x}{\cos^2 x}$
$=-\dfrac{1}{\sin^2 x}$ [∵ sin2 x+cos2 x=1]
= -cosec2x.
Thus, the derivative of cot x by the quotient rule is -cosec2 x.
Derivative of cot x by Chain Rule
We can express cot x = 1/tan x. Using this fact we can find the derivative of cot x by the chain rule.
Let $t = \tan x$. So we have $\dfrac{dt}{dx}= \sec^2 x$.
∴ $\dfrac{d}{dx}(\cot x) = \dfrac{d}{dx}\Big(\dfrac{1}{\tan x} \Big) = \dfrac{d}{dx}\Big(\dfrac{1}{t} \Big)$
⇒ $\dfrac{d}{dx}(\cot x) = \dfrac{d}{dx}\Big(\dfrac{1}{t} \Big)$
= $\dfrac{d}{dt}\Big(\dfrac{1}{t} \Big) \cdot \dfrac{dt}{dx}$, by the chain rule of derivatives
= $\dfrac{d}{dt}(t^{-1}) \cdot \dfrac{dt}{dx}$
= (-t-1-1) . sec2 x by the power rule of derivatives
= -1/t2 . sec2 x
= -1/tan2 x . sec2 x
= $-\dfrac{\cos^2 x}{\sin^2 x} \cdot \dfrac{1}{\cos^2 x}$
= -1/sin2x
= -cosec2 x.
So the derivative of cot x by the chain rule is -cosec2 x.
Solved Problems on Derivative of cot x
Question 1: What is the derivative of cot(x2).
Solution:
Let t =x2. Thus, dt/dx =2x.
Now, the derivative of cot(x2) by chain rule is equal to
$\dfrac{d}{dx}$(cot x2) = $\dfrac{d}{dt}$(cot t) · $\dfrac{dt}{dx}$ = -cosec2t · 2x = -2x cosec2(x2) as t=x2.
Answer: The derivative of cot(x2) is -2x cosec2(x2).
Question 2: Find the derivative of cot x with respect to tan x.
Solution:
Let u=cot x and v=tan x. Here, we need to find du/dv.
Note that $\dfrac{du}{dx}$ = -cosec2x and $\dfrac{dv}{dx}$ = sec2 x
⇒ $\dfrac{dx}{dv}$ = 1/sec2 x = cos2x.
So the derivative of cot x with respect to tan x is
$\dfrac{d}{d(\tan x)}(\cot x)=\dfrac{du}{dv}$
= $\dfrac{du}{dx}$ · $\dfrac{dx}{dv}$
= -cosec2x · cos2x = – (cos2 x)/(sin2 x) = -cot2x.
Answer: the derivative of cot x with respect to tan x is -cot2x.
Question 3: Find the derivative of x cot x.
Solution:
By the chain rule of derivatives, the derivative of xcotx is equal to
d(x cot x)/dx = x d(cot x)/dx + cot x dx/dx
= x (-cosec2x) + cot x · 1
= –x cosec2x + cot x
Answer: The derivative of xcotx is –x cosec2x + cot x.
FAQs on Derivative of cot x
Answer: The derivative of cot x is -cosec2x.
Ans: Note that cot2x = (cot x)2. So by the power rule and the chain rule of derivatives, the derivative of cot2x is equal to d(cot2x)/dx = 2 cot x · d/dx(cot x) = -2 cot x cosec2x.
Ans: The integration of tan x is ln|sin x| + C.
Ans: The derivative of cot-1x is -1/(1+x2).
This article is written by Dr. T, an expert in Mathematics (PhD). On Mathstoon.com you will find Maths from very basic level to advanced level. Thanks for visiting.